If you are trying to grow your small business, proper strategic planning goes a long way. One strategic tool that is simple and effective is the Ansoff Matrix. Initially developed by Igor Ansoff in 1957, this matrix has become a cornerstone for business growth strategies used by fledgling startups and mature businesses.
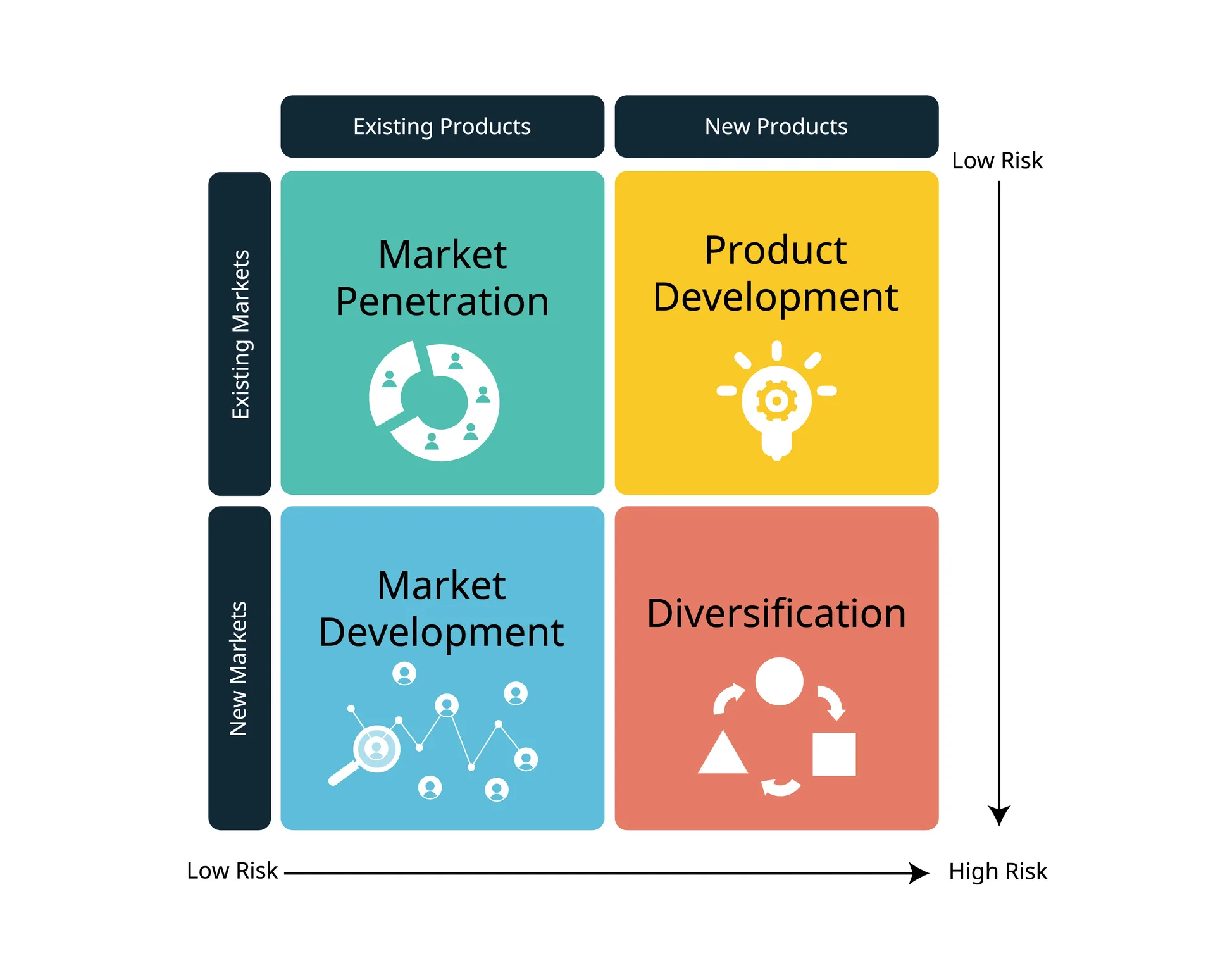
But what exactly is the Ansoff Matrix, and how can it be leveraged by small businesses to carve out a path for growth and success? The Ansoff Matrix is a framework that helps companies strategize their growth by focusing on four key areas: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. Each of these areas offers unique opportunities and challenges, particularly for small businesses that often operate with limited resources but have the advantage of agility and innovation.
This article will explore the Ansoff Matrix and offer practical advice for the small business owner. We will discuss the four strategies and offer insights into how they can be effectively applied in a smaller enterprise. Whether you’re looking to deepen your foothold in existing markets, introduce exciting new products, venture into uncharted territories, or diversify your business portfolio, understanding the Ansoff Matrix can be your first step toward strategic growth.
The Four Strategies of the Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a tool that breaks down business growth strategies into four distinct categories. Understanding each of these is helpful for small business owners looking to make informed decisions about their growth paths. Let’s explore these strategies in detail.
A. Market Penetration
Market penetration is about growing your business within the existing market space. It involves strategies to increase your share in the current market where your products or services are already offered. This approach is often seen as the ‘safest’ of the four strategies, as it builds on what you already know and do.
- Definition and Explanation
Market penetration focuses on selling more existing products or services to your current market. This could involve tactics like price adjustments, promotional activities, improved customer service, or enhancing product features.
- Examples for Small Businesses
- Offering discounts or loyalty rewards to existing customers.
- Enhancing online marketing efforts to increase visibility among current customers.
- Refining the product based on customer feedback to encourage repeat purchases.
- Benefits and Challenges
Benefits: Lower risk since you are dealing with familiar products and markets; potentially faster results.
Challenges: The market size is limited, intense competition, and the risk of market saturation.
B. Product Development
Product development is about innovation and introducing new products or services to your current market. It’s a step beyond market penetration, where you start to expand your offerings.
- Definition and Explanation
This strategy involves developing new products or significantly improving existing ones to meet the evolving needs of your current market. It can include anything from launching an entirely new product line to making incremental improvements to existing products.
- Examples for Small Businesses
- Developing a new product line that complements the existing offerings.
- Incorporating new technology into existing products to enhance functionality.
- Collaborating with other businesses to create joint products.
- Advantages and Potential Pitfalls
Advantages: Opportunity to capture more market share; differentiation from competitors; fostering innovation.
Pitfalls: Higher risk compared to market penetration; requires research and development investment; uncertainty in customer acceptance.
C. Market Development
Market development involves taking your existing products or services into new markets. This could mean expanding to new geographical areas, targeting different customer segments, or finding new uses for your product.
- Definition and Explanation
This strategy is about finding new markets for your current products. It could involve geographic expansion, targeting new demographics, or exploring new distribution channels.
- Strategies for Small Businesses
- Expanding to online sales to reach a broader audience.
- Identify and target a new demographic that may benefit from existing products.
- Collaborating with businesses in different regions for market access.
- Pros and Cons
Pros: Access to new customers; reduced dependence on a single market; potential for significant growth.
Cons: Requires market research and understanding of new markets, potential cultural and logistical challenges, and increased marketing costs.
D. Diversification
Diversification is the most adventurous of the four strategies. It involves venturing into entirely new products and new markets. It’s about charting unknown territories with the potential for high rewards and increased risks.
- Definition and Explanation
Diversification means offering new products or services to new markets. It’s about branching out into areas unrelated to your current business operations.
- Identifying Opportunities for Small Businesses
- Exploring business sectors that are complementary to your current industry.
- Partnering with other businesses to venture into different markets.
- Investing in emerging technologies or trends.
- Risks and Rewards
Risks: High level of uncertainty; significant investment in research and development; potential for spreading resources too thin.
Rewards: Potential for opening up entirely new revenue streams, reducing risk by diversifying business interests, and opportunities for significant business growth.
For small business owners, these strategies offer a path for growth, each with unique opportunities and challenges. Whether deepening your market presence, innovating your product line, exploring new markets, or venturing into entirely new territories, the Ansoff Matrix provides a structured approach to strategize your business growth.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into how you can apply these strategies to your small business, including conducting market analysis and aligning your business goals with the right strategy.
Applying the Ansoff Matrix to Your Small Business
Understanding the Ansoff Matrix is one thing; applying it effectively to your small business is another. This section guides you through the practical steps to leverage the Ansoff Matrix for your business growth.
Conducting a Market Analysis
A thorough market analysis is essential before diving into any of the Ansoff strategies. This will help you understand your current market position, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions.
- Steps for Effective Market Analysis
- Identify Your Target Market: Understand customers’ needs and buying behaviors.
- Analyze Competitors: Know who your competitors are, what they offer, and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about the latest trends and how they might affect your business and industry.
- Customer Feedback: Gather and analyze feedback from your existing customers to understand their satisfaction and needs.
Aligning Business Goals with Ansoff Strategies
Each Ansoff strategy aligns with different business goals. Your choice of strategy should reflect where you want your business to go.
- Matching Goals to Strategies
- For Market Penetration: Ideal if your goal is to increase sales or market share in your existing market.
- For Product Development: Suited for goals related to innovation, expanding product lines, or improving customer satisfaction.
- For Market Development: Choose this if your goal is to expand into new markets or regions.
- For Diversification: Opt for this if your goal is to explore new business opportunities and reduce reliance on current markets.
This section outlines the practical steps to apply the Ansoff Matrix strategies to your small business, from conducting market analysis to aligning your goals with the right strategy. The following section will explore how to navigate challenges and risks associated with each plan, ensuring you’re well-equipped to make the best decisions for your business’s growth.
Navigating Challenges and Risks in the Ansoff Matrix Strategies
While the Ansoff Matrix provides a valuable framework for business growth, each strategy has challenges and risks. Being aware of these and knowing how to navigate them is crucial for successful implementation.
Understanding and Mitigating Risks in Each Strategy
Each Ansoff strategy has inherent risks that must be understood and managed effectively.
- Market Penetration Risks
- Saturation: The risk of the market becoming saturated, leaving little room for growth.
- Intense Competition: Facing tough competition as you try to increase your market share.
- Risk Mitigation: Focus on differentiating your business and offering unique value to customers. Keep an eye on market trends to avoid saturation.
- Product Development Risks
- High Development Costs: The financial burden of developing new products can be significant.
- Uncertain Market Acceptance: There’s always a risk that the market may not accept your new product.
- Risk Mitigation: Conduct thorough market research and prototype testing before full-scale development. Engage with customers early in the development process.
- Market Development Risks
- Cultural Differences: Expanding into new markets may require understanding and adapting to different cultural norms.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different markets may have varying regulations and compliance requirements.
- Risk Mitigation: Research the new market thoroughly, including cultural and regulatory aspects. Consider partnerships with local businesses for better market entry.
- Diversification Risks
- Straying Too Far from Core Competencies: Diversifying into areas where you lack expertise can be risky.
- Resource Allocation: Diversification can strain your resources, including finances and personnel.
- Risk Mitigation: Ensure diversification aligns with your business vision and capabilities. Plan resource allocation carefully to avoid overextension.
Balancing Ambition with Practicality
Balancing ambitious growth goals with the practical realities of running a small business is essential when applying Ansoff’s strategies.
- Practical Considerations
- Financial Constraints: Be realistic about what you can afford regarding investment and risk.
- Resource Limitations: Understand the limitations of your current resources, including staff, technology, and time.
- Market Readiness: Assess whether the market is ready for your growth efforts, be it a new product or entering a new market.
- Achieving Sustainable Growth
- Incremental Steps: Consider taking smaller, more manageable steps toward your growth goals.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and adjust your strategies based on market feedback and business performance.
Learning from Common Mistakes
Observing the common pitfalls in applying the Ansoff Matrix can save you from making similar errors.
- Overexpansion
- Symptoms: Rapid expansion that outpaces your business’s ability to manage effectively.
- Prevention: Grow at a pace that aligns with your ability to maintain quality and customer service.
- Neglecting Core Business
- Symptoms: Losing focus on your current successful operations while chasing new opportunities.
- Prevention: Ensure that new growth strategies do not detract from what already works well for your business.
- Misreading the Market
- Symptoms: Misinterpreting market signals and customer feedback, leading to misguided strategies.
- Prevention: Invest in accurate market research and stay closely connected to customer feedback.
Conclusion
As a small business owner, charting a growth path using the Ansoff Matrix can be exciting and challenging. Understanding the risks and challenges associated with each strategy, balancing ambition with practicality, and learning from common mistakes are vital to successfully applying this framework. By doing so, you can make strategic choices that lead to sustainable growth and a stronger, more resilient business.
Share with:








